
1
You may be eligible for Social Security
benets by earning Social Security
credits when you work in a job and pay
Social Security taxes.
We base Social Security credits on the
amount of your earnings. We use your
earnings and work history to determine
your eligibility for retirement or disability
benets or your family’s eligibility for
survivors benets. We cannot pay
benets if you don’t have enough credits.
In 2024, you receive 1 credit for each
$1,730 of earnings, up to the maximum
of 4 credits per year.
Each year the amount of earnings
needed for credits goes up slightly as
average earnings levels increase. The
credits you earn remain on your record
even if you change jobs or have no
earnings for a while.
Special rules for some jobs
Special rules for earning Social Security
coverage apply to certain types of work.
If you are self-employed, you earn
Social Security credits the same way
employees do (1 credit for each $1,730
in net earnings, but no more than 4
credits per year). Special rules apply
if you have net annual earnings of
less than $400. For more information,
read If You Are Self-Employed
(Publication No. 05-10022).

2
If you are in the military, you earn
Social Security credits the same way
civilian employees do. You may also get
additional earnings credits under certain
conditions. For more information, read
Military Service and Social Security
(Publication No. 05-10017).
We also have special rules about how
you earn credits for other kinds of work.
Some of these are:
• Domestic work.
• Farm work.
• Work for a nonprot or religious
organization that does not pay Social
Security taxes.
Contact us if you have a question about
how you earn credits in your job.
How long you must work to be
eligible for Social Security
The number of credits you need to be
eligible for benets depends on your age
and the type of benet.
Retirement benets
Anyone born in 1929 or later needs 10
years of work (40 credits) to be eligible
for retirement benets.
Disability benets
How many credits you need for disability
benets depends on how old you are
when your disability began.
3
• If you develop a disability before age
24, you generally need 1½ years of
work (6 credits) in the 3 years before
your disability began.
• If you are between ages 24 through
30, you generally need credits for ½ of
the time between age 21 and the time
your disability began.
• A person with a qualifying disability
at age 31 or older, generally needs
at least 20 credits in the 10 years
immediately before their disability
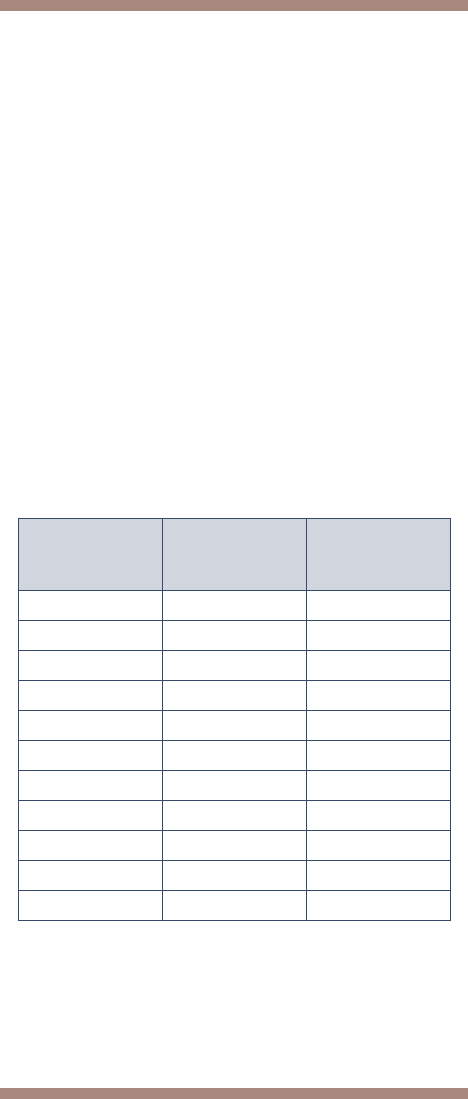
began. The following table shows
examples of how many credits you
would need if you develop a disability
at various selected ages. This table
does not cover all situations.
Developed
a disability
at age
Credits
needed
Years of
work
31 through 42 20 5
44 22 5 ½
46 24 6
48 26 6 ½
50 28 7
52 30 7 ½
54 32 8
56 34 8 ½
58 36 9
60 38 9 ½
62 or older 40 10
Survivors benets
When a person who has worked and
paid Social Security taxes dies, certain
members of the family may be eligible for

4
survivors benets. Up to 10 years of work
are required to be eligible for benets,
depending on the person’s age at the time
of death. Survivors of very young workers
may be eligible if the deceased worker
was employed for 1½ years during the 3
years before their death.
Social Security survivors benets can be
paid to:
• A surviving spouse — full benets
at full retirement age, or reduced
benets as early as age 60.
• A surviving spouse with a disability —
as early as age 50.
• A surviving spouse of any age who
takes care of the deceased’s child.
This child must be younger than age
16 or have a disability, and receive
Social Security benets.
• Surviving divorced spouses under
certain conditions.
• Unmarried children younger than
age 18, or up to age 19 if they attend
elementary or secondary school full
time. Under certain circumstances,
benets can be paid to stepchildren,
grandchildren, or adopted children.
• Unmarried children age 18 or older
who developed a disability before age
22 and whose condition(s) remains
the same.
• Dependent parents age 62 or older.
Contact us if you need more information
about your family’s situation.

5
(over)
Medicare
The Social Security credits you earn
also count toward eligibility for Medicare
when you reach age 65. You may be
eligible for Medicare at an earlier age if
you get disability benets for 24 months
or more. Those who have permanent
kidney failure or get disability benets
because of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
(Lou Gehrig’s disease) do not have to
wait 24 months to receive Medicare
coverage. Your dependents or survivors
may also be eligible for Medicare at age
65 or earlier if they have a qualifying
disability. People who have permanent
kidney failure and need kidney dialysis
or a kidney transplant may be eligible
for Medicare at any age. This is based
on a spouse’s or parent’s earnings
as well as their own. If you would like
more information about Medicare, read
Medicare (Publication No. 05-10043).
Not every kind of work counts
toward Social Security benets
Not all employees work in jobs covered
by us. Examples of some of these
employees are:
• Most federal employees hired before
1984. Since January 1, 1983, all
federal employees have paid the
Medicare hospital insurance part
of the Social Security tax. Railroad
employees with more than 10 years
of service.

6
• Employees of some state and local
governments that chose not to
participate in Social Security.
• Children younger than age 21 who do
household chores for a parent (except
a child age 18 or older who works in
the parent’s business).
Make sure your records
are accurate
Each year, your employer sends a copy
of your W-2 (Wage and Tax Statement)
to us. We compare your name and
Social Security number (SSN) on the
W-2 with our records. Your earnings
shown on the W-2 are recorded on
your permanent earnings record. Your
earnings record is what we use to gure
whether you can get future benets and
the benet amount.
Your name and SSN on your Social
Security card must agree with the
information on your employer’s payroll
records and W-2. Protect your future
benets by making sure both records are
correct. Tell your employer if your name
or SSN is incorrect on the employer’s
record. If your Social Security card is
not correct, contact any Social Security
ofce.
Contacting Us
The most convenient way to do business
with us is to visit www.ssa.gov to
get information and use our online
services. There are several things you

7
can do online: apply for benets; start
or complete your request for an original
or replacement Social Security card;
get useful information; nd publications;
and get answers to frequently asked
questions.
When you open a personal
my Social Security account, you have
more capabilities. You can review
your Social Security Statement, verify
your earnings, and get estimates of
future benets. You can also print
a benet verication letter, change
your direct deposit information (Social
Security beneciaries only), and get a
replacement SSA-1099/1042S. Access
to your personal my Social Security
account may be limited for users outside
the United States.
If you don’t have access to the internet,
we offer many automated services by
telephone, 24 hours a day, 7 days a
week, so you may not need to speak
with a representative.
If you need to speak with someone, call
us toll-free at 1-800-772-1213 or at our
TTY number, 1-800-325-0778, if you’re
deaf or hard of hearing. A member of
our staff can answer your call from 8
a.m. to 7 p.m., Monday through Friday.
We provide free interpreter services
upon request. For quicker access to a
representative, try calling early in the
day (between 8 a.m. and 10 a.m. local
time) or later in the day. We are less
busy later in the week (Wednesday to
Friday) and later in the month.

8
Notes

Social Security Administration
Publication No. 05-10072
January 2024 (Recycle prior editions)
How You Earn Credits
Produced and published at U.S. taxpayer expense

