Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
List of Changes
All changes to paragraphs, tables, and figures in this document are shown below;
Release Date
Revision
Paragraph(s)
Rationale
November 20
th
, 2019
1.0
All
-
December 25
th
, 2019
2.0
All
Changed
expressions and
corrected typos
2. Setting up your machine
Updated for
Windows users
3.1.1. Game APIs
Updated API
details
4.3. Upload APK and run your program
4.4. Check result
Updated
contents and
figures
4.5. Run on your machine (optional)
Added
5. Tips for programming
Added some
important tips
January 29
th
, 2020
2.1
3.1. Creating an Android project
Added notes
4.4. Checking simulation while running
Moved Section
from Chapter 4.5
4.5.4. rosbag replay settings
Added
March 12
th
, 2020
2.2
3.1.1. Game APIs
4.6.3. Setting up the Astrobee Robot
Software
Added notes
4.6.1. Differences between web
simulator and local simulator
6. Simulator change log
Added
3.1.2 (3) Reference
4.6.5. Building the Guest Science
Manager APK
Fix github URL
4.6.9 (3) Running the Guest Science
Manager APK and GS APK
Fixed gds
manager path
March 30
th
, 2020
2.3
3.2.3. How to change the application id
(option)
5.4. About navigation error
Added
2.2.2. Installing Android Studio
Add Android
Studio version
4.4. Checking simulation while running
Corrected
simulation speed
0.5x to 1.0x(real-
time)
June 26
th
, 2020
2.3.1
3.1.1 Game APIs
judgeSendDiscoveredQR
Corrected the
description about
Final round
August 5
th
, 2020
2.3.2
3.2.3. Change the application ID
(optional)
Add 10
th
Step
August 21
st
, 2020
2.3.3
3.1.1 Game APIs
Add Flashlight
Control APIs

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
Contents
1. Introduction ............................................................................................................................... 1
2. Setting up your machine ............................................................................................................ 2
2.1. Requirements ..................................................................................................................... 2
2.2. Setting up Android Studio.................................................................................................... 2
2.2.1. Installing components (Only on Ubuntu) .......................................................................... 2
2.2.2. Installing Android Studio................................................................................................... 2
2.2.3. Downloading additional components ................................................................................ 3
3. Creating your application ........................................................................................................... 4
3.1. Creating an Android project ................................................................................................. 4
3.1.1. Game APIs ....................................................................................................................... 4
(1) Writing the application ....................................................................................................... 4
(2) API details ......................................................................................................................... 6
3.1.2. Type information ............................................................................................................ 14
(1) Summary ........................................................................................................................ 14
(2) Details ............................................................................................................................. 14
(3) Reference ....................................................................................................................... 16
3.2. Building your application ................................................................................................... 17
3.2.1. On Ubuntu ..................................................................................................................... 17
3.2.2. On Windows .................................................................................................................. 17
3.2.3. Change the application ID (optional) .............................................................................. 18
(1) On Ubuntu ...................................................................................................................... 21
(2) On Windows ................................................................................................................... 21
4. Running your program on the simulator ................................................................................... 22
4.1. Using the simulator server ................................................................................................ 22
4.2. Login ................................................................................................................................. 22
4.3. Uploading the APK and running your program .................................................................. 24
4.4. Checking simulation while running .................................................................................... 25
4.5. Checking the result ........................................................................................................... 26
4.5.1. Result summary ............................................................................................................. 26
4.5.2. Download ZIP file ........................................................................................................... 27
4.5.3. Check simulation after running ....................................................................................... 28
4.5.4. rosbag replay settings .................................................................................................... 29
4.5.5. rviz settings .................................................................................................................... 30
4.6. Running on your own machine (optional) .......................................................................... 31
4.6.1. Differences between web simulator and local simulator ................................................. 31
4.6.2. Requirements ................................................................................................................ 31
4.6.3. Setting up the Astrobee Robot Software ........................................................................ 31
4.6.4. Creating the AVD ( Android Virtual Device ) ................................................................... 33
4.6.5. Building the Guest Science Manager APK ..................................................................... 34

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
4.6.6. Setting up the network ................................................................................................... 34
(1) Setting the HOST network .............................................................................................. 34
(2) Setting the environment variables ................................................................................... 34
(3) Setting up the Android network and starting the Android Emulator .................................. 35
4.6.7. Installing APKs ............................................................................................................... 35
4.6.8. Setting QR codes, an AR tag, and the target .................................................................. 35
4.6.9. Running your program ................................................................................................... 36
(1) Launching the Android Emulator ..................................................................................... 36
(2) Starting the Astrobee Simulator ....................................................................................... 36
(3) Running the Guest Science Manager APK and GS APK ................................................. 37
5. Programming tips .................................................................................................................... 38
5.1. Do NOT write infinite loops ............................................................................................... 38
5.2. Dealing with randomness .................................................................................................. 39
5.3. Camera parameters .......................................................................................................... 40
5.4. About navigation error ....................................................................................................... 40
6. Simulator change log ............................................................................................................... 41

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
1
1. Introduction
Let's start programming!
Astrobee can be controlled with an Android application called the Guest Science APK
(GS APK). First, setup your machine to build your application according to the instructions
in Chapter 2. Next, read Chapter 3 and create a GS APK. This chapter explains the game
APIs that operate Astrobee, such as moving Astrobee and getting camera images. Then,
try running the GS APK in the simulator environment. Chapter 4 describes how to use the
environment.

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
2
2. Setting up your machine
First of all, set up a machine for programming.
2.1. Requirements
The machine must meet the following requirements.
64-bit processor
4 GB RAM (8 GB RAM recommended)
Ubuntu 16.04 (64-bit version) ( http://releases.ubuntu.com/16.04/ )
or Windows 10 (64-bit version)
NOTE: If you want to run your program on your own PC, you need 8 GB of RAM (16 GB
RAM recommended) and Ubuntu 16.04. For details, please refer to 0
2.2. Setting up Android Studio
2.2.1. Installing components (Only on Ubuntu)
If you use an Ubuntu machine, you need these components.
openJDK8
ADB (Android Debug Bridge)
Gradle
Please install them with the following command.
sudo apt-get -y install openjdk-8-jdk adb gradle
2.2.2. Installing Android Studio
Please download Android Studio 3.4.1 from Android Studio download archives page
( https://developer.android.com/studio/archivehttps://developer.android.com/studio/index.ht
ml ) and extract it into your home directory.

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
3
2.2.3. Downloading additional components
To build the Guest Science APK, you need to download additional components as
follows.
1) Launch Android Studio.
2) Select [Tools] -> [SDK Manager].
3) On the SDK Platforms Tab, check “show Package Details”. Select “Android SDK
Platform 25” and “Android SDK Platform 26”.
4) On the SDK Tools Tab, check “show Package Details”. Select “25.0.3”, “26.0.2”
under Android SDK Build-Tools and “Android SDK Platform-Tools”.
5) Click the [Apply] button to install these components.
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
4
3. Creating your application
3.1. Creating an Android project
To create your application, prepare a new project with the following steps.
1) Download APK template (Template APK) from the Download page on the Web site.
2) Extract the zip file to the directory where you want it.
3) Launch Android Studio.
4) Open the APK template folder with [File] -> [Open].
5) Open [app/java/jp.jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc.defaultapk /YourService.java] in Project view.
6) Write your code in runPlan1 – runPlan3 methods in the YourService.java file.
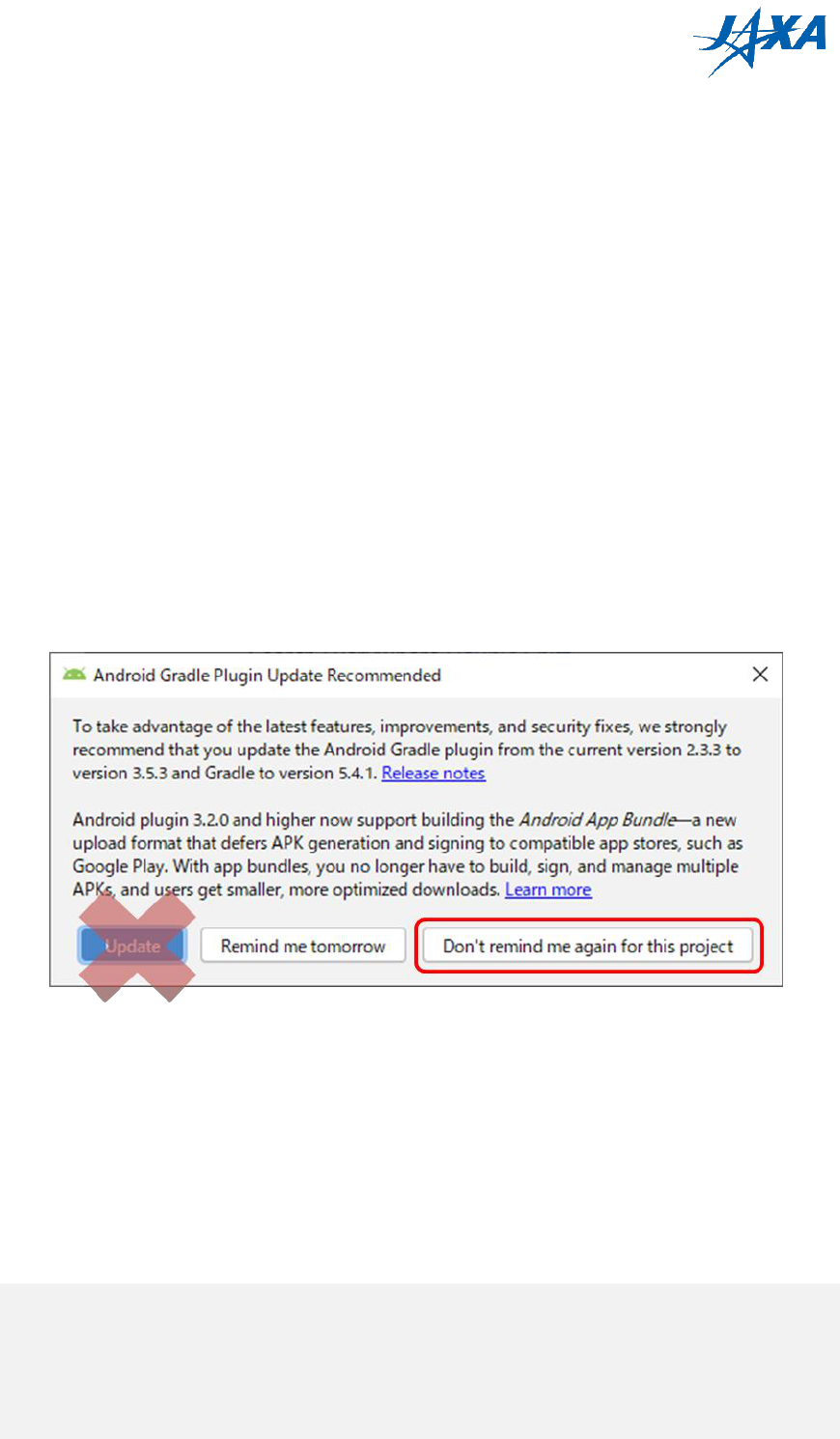
When you open APK template folder, “Android Gradle Plugin Update Recommended”
dialog may appear. However you must not update because of dependency problem, so
push “Don’t remind me again for this project”
Figure 3.1-1 Android Gradle Plugin Update Recommended dialog
3.1.1. Game APIs
(1) Writing the application
You can use the game APIs shown below in the YourService.java file.
“runPlan1” is executed on the web simulator. You can choose any plan when you run
the application on your own machine.
public class YourService extends KiboRpcService {
// write your plan 1 here
@Override
protected void runPlan1(){

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
5
// start this run
api.judgeSendStart();
// move Astrobee from the starting point to P1-1
Point point = new Point(1.1, -2.2, 3.3);
Quaternion quaternion = new Quaternion(4.4, -5.5, 6.6, -7.7);
api.moveTo(point, quaternion, true);
// :
// once Astrobee came to P1-1, get a camera image
Bitmap snapshot = api.getBitmapNavCam();
// read the QR code in the image and get the x-axis coordinate value of P3
String valueX = …;
// send the result to scoring module
api.judgeSendDiscoveredQR(0, valueX);
// implement some other functions or repeat for P1-2, P1-3, …
// :
// once Astrobee came to P3, get a camera image
Bitmap snapshot = api.getBitmapNavCam();
// read the AR tag in the image
String markerId = …;
// send the result to the scoring module
api.judgeSendDiscoveredAR(markerId);
// some other functions
// :
// turn on the laser light,
api.laserControl(true);
// take snapshots to evaluate the accuracy of laser pointing and finish this run
api.judgeSendFinishSimulation();
sendData(MessageType.JSON, "data", "SUCCESS:defaultapk runPlan1");
}
// write your other plans here
// …
}
You can find methods of the game APIs by using the code completion function of
Android Studio.
Please refer to (2) for more information and you can download Sample APK from the
Download page on the Web site.
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
6
(2) API details
Details of the Kibo-RPC’s game APIs are listed below.
(2-1) Method Summary
Table 3-1 Method Summary
Modifier and Type
Method and Description
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.Re
sult
flashlightControlFront (float brightness)
Set Brightness of Front Flash Light
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.Re
sult
flashlightControlBack (float brightness)
Set Brightness of Back Flash Light
android.graphics.Bitmap
getBitmapDockCam()
Get Bitmap image of DockCam.
android.graphics.Bitmap
getBitmapNavCam()
Get Bitmap image of NavCam.
jp.jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc.api
.types.ImuResult
getImu()
Get IMU telemetry
static KiboRpcApi
getInstance(gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.android.gs
.StartGuestScienceService startGuestScienceS
ervice)
Static method that provides a unique instance of this class
org.opencv.core.Mat
getMatDockCam()
Get Mat image of DockCam.
org.opencv.core.Mat
getMatNavCam()
Get Mat image of NavCam.
jp.jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc.api
.types.PointCloud
getPointCloudHazCam()
Get PointCloud data of HazCam.
jp.jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc.api
.types.PointCloud
getPointCloudPerchCam()
Get PointCloud data of PerchCam.
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.Ki
nematics
getTrustedRobotKinematics()
Get trusted data related to positioning and orientation for
Astrobee with infinite timeouts
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.Ki
nematics
getTrustedRobotKinematics(int timeout)
Get trusted data related to positioning and orientation for
Astrobee
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
7
Modifier and Type
Method and Description
void
judgeSendDiscoveredAR(java.lang.String id)
Send an AR ID for judge.
void
judgeSendDiscoveredQR(int no,
java.lang.String value)
Send a QR code data for judge.
void
judgeSendFinishISS()
Send finish command to do final operation at ISS.
void
judgeSendFinishSimulation()
Send finish command to do final operation in simulation.
void
judgeSendStart()
Send a starting time stamp for judge.
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.Re
sult
moveTo(gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.types.Point goa
lPoint,
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.types.Quaternion orien
tation, boolean printRobotPosition)
Move Astrobee to the given point and rotate it to the given
orientation.
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.Re
sult
relativeMoveTo(gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.types.P
oint goalPoint,
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.types.Quaternion orien
tation, boolean printRobotPosition)
Move Astrobee to the given point using a relative reference
and rotates it to the given orientation.
void
shutdownFactory()
This method shutdown the robot factory in order to allow
java to close correctly.

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
8
(2-2) Method Details
• flashlightControlFront
public gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.Result flashlightControlFront
(float brightness)
Brightness of Front Flashlight
Parameters:
brightness - Brightness percentage between 0 - 1.
Returns:
A Result instance carrying data related to the execution.
Returns null if the command was NOT executed as a result of
an error
• flashlightControlBack
public gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.Result flashlightControlBack
(float brightness)
Brightness of Back Flashlight
Parameters:
brightness - Brightness percentage between 0 - 1.
Returns:
A Result instance carrying data related to the execution.
Returns null if the command was NOT executed as a result of
an error
• shutdownFactory
public void shutdownFactory()
This method shuts down the robot factory in order to allow java to close correctly.
• getInstance
public
static KiboRpcApi getInstance(gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.android.gs.Sta
rtGuestScienceService startGuestScienceService)
Static method that provides a unique instance of this class
Returns:
A unique instance of this class ready to use
• getTrustedRobotKinematics
public gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.Kinematics getTrustedRobotKinematics(
int timeout)
Gets trusted data related to positioning and orientation for Astrobee
Parameters:
timeout - Number of seconds before canceling request
Returns:
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
9
Kinematics Trusted Kinematics, null if an internal error
occurred or request timeout
• getTrustedRobotKinematics
public gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.Kinematics getTrustedRobotKinematics(
)
Gets trusted data related to positioning and orientation for Astrobee with infinite timeouts
Returns:
Kinematics Trusted Kinematics, null if an internal error
occurred or request timeout
• getImu
public jp.jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc.api.types.ImuResult getImu()
Gets IMU telemetry
Returns:
ImuResult data, null if an internal error occurred.

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
10
• getBitmapNavCam
public android.graphics.Bitmap getBitmapNavCam()
Gets Bitmap image of NavCam.
Returns:
Bitmap image of NavCam(1280 px x 960 px), null if an internal
error occurred. Format:Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888
• getBitmapDockCam
public android.graphics.Bitmap getBitmapDockCam()
Gets Bitmap image of DockCam.
Returns:
Bitmap image of DockCam(1280 px x 960 px), null if an
internal error occurred. Format:Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888
• getMatNavCam
public org.opencv.core.Mat getMatNavCam()
Gets Mat image of NavCam.
Returns:
Mat image of NavCam(1280 px x 960 px), null if an internal
error occurred. Format:CV8UC1
• getMatDockCam
public org.opencv.core.Mat getMatDockCam()
Gets Mat image of DockCam.
Returns:
Mat image of DockCam(1280 px x 960 px), null if an internal
error occurred. Format:CV8UC1
• getPointCloudHazCam
public jp.jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc.api.types.PointCloud getPointCloudHazC
am()
Gets PointCloud data of HazCam.
Returns:
PointCloud data of HazCam(224 px x 171 px), null if an
internal error occurred.
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
11
• getPointCloudPerchCam
public jp.jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc.api.types.PointCloud getPointCloudPerc
hCam()
Gets PointCloud data of PerchCam.
Returns:
PointCloud data of PerchCam(224 px x 171 px), null if an
internal error occurred.
• moveTo
public gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.Result moveTo(gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.t
ypes.Point goalPoint,
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.types.Quaternion orientation,
boolean printRobotPosition)
Moves Astrobee to the given point and rotates it to the given orientation.
Parameters:
goalPoint - Absolute cardinal point (xyz)
orientation - An instance of the Quaternion class. You may
want to use CENTER_US_LAB or CENTER_JEM as an example
depending on your initial position.
printRobotPosition - flag which print robot positions in log
or not.
Returns:
A Result instance carrying data related to the execution.
Returns null if the command was NOT executed as a result of
an error
• relativeMoveTo
public gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.Result relativeMoveTo(gov.nasa.arc.as
trobee.types.Point goalPoint,
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.types.Quaternion orientation,
boolean printRobotPosition)
Moves Astrobee to the given point using a relative reference and rotates it to the given
orientation.
Parameters:
goalPoint - The relative end point (relative to Astrobee)
orientation - The absolute orientation
printRobotPosition - flag which print robot positions in log
or not.
Returns:
A Result instance carrying data related to the execution.
Returns null if the command was NOT executed as a result of
an error
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
12
• laserControl
public gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.Result laserControl(boolean state)
Turns power on/off Laser Pointer. If it is same state as input parameter, nothing happens.
Parameters:
state - Set a laser pointer true:power on / false:power off.
Returns:
A Result instance carrying data related to the execution.
Returns null if the command was NOT executed as a result of
an error
• judgeSendStart
public void judgeSendStart()
Sends a starting time stamp for scoring.
You should call this function before you start your mission, otherwise your score is not
calculated.
• judgeSendFinishSimulation
public void judgeSendFinishSimulation()
Sends finish command to do final operation in simulation. When this function is called,
snapshots of laser pointing accuracy are taken and they are used to scoring.
You should call this function once you have turned the laser on, otherwise your score is not
calculated.
• judgeSendFinishISS
public void judgeSendFinishISS()
Sends finish command to do final operation at ISS. This function is for final round.
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
13
• judgeSendDiscoveredQR
public void judgeSendDiscoveredQR(int no,
java.lang.String value)
Sends a QR code data for scoring.
Warning:
1, Each pair of no and value is accepted only once.You should call this function once each
QR code has been discovered,otherwise your score is not calculated.
2, You DO NOT change a value read from QR code, you should send a raw string you read.
Parameters:
no - QR code number.
[Preliminary round, Simulation]
0:pos_x, 1:pos_y, 2:pos_z 3:qua_x, 4:qua_y, 5:qua_z
[Final round, ISS]
0:pos_x, pos_y, pos_z
1:qua_x, qua_y, qua_z
value - string you read from QR code.
[Preliminary round, Simulation]
ex: pos_x, 1.23456
[Final round, ISS]
ex: pos_x, 1.23456, pos_y, 2.3456789, pos_z, 3.456
• judgeSendDiscoveredAR
public void judgeSendDiscoveredAR(java.lang.String id)
Sends an AR ID for scoring.
You should call this function once an AR tag has been discovered, otherwise your score is
not calculated
Parameters:
id - AR code id you read.
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
14
3.1.2. Type information
(1) Summary
Table 3-2 Type information summary
Type
Description
jp.jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc.api
.types.ImuResult
IMU telemetry data.
jp.jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc.api
.types.PointCloud
Point cloud data.
(2) Details
Details of Kibo-RPC’s types are bellow.
(2-1) jp.jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc.api.types.ImuResult
• getAngularVelocity
public gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.types.Vec3d getAngularVelocity()
Returns:
Angular velocity data.
• getAngularVelocityCovariance
public double[] getAngularVelocityCovariance()
Returns:
Angular velocity Covariance data.
• getLinearAcceleration
public gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.types.Vec3d getLinearAcceleration()
Returns:
Linear acceleration data.
• getLinearAccelerationCovariance
public double[] getLinearAccelerationCovariance()
Returns:
Linear acceleration covariance data.
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
15
• getOrientation
public gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.types.Quaternion getOrientation()
Returns:
Orientation data.
• getOrientationCovariance
public double[] getOrientationCovariance()
Returns:
Orientation covariance.
(2-2) jp.jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc.api.types.PointCloud
• getWidth
public int getWidth()
Returns:
Width of point cloud data.
• getHeight
public int getHeight()
Returns:
Height of point cloud data.
• getPointArray
public gov.nasa.arc.astrobee.types.Point[] getPointArray()
Returns:
Point arrays of point cloud data. It contains number of array
data Width times Height.
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
16
(3) Reference
Please refer below for information about other Types.
Type
URL
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee
.Kinematis
https://github.com/nasa/astrobee_android/blob/5b07e4d626781
a6f7e0a9cdf4397375cbe509803/astrobee_api/api/src/main/jav
a/gov/nasa/arc/astrobee/Kinematics.java
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee
.Result
https://github.com/nasa/astrobee_android/blob/5b07e4d626781
a6f7e0a9cdf4397375cbe509803/astrobee_api/api/src/main/jav
a/gov/nasa/arc/astrobee/Result.java
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee
.types.Vec3d
https://github.com/nasa/astrobee_android/blob/5b07e4d626781
a6f7e0a9cdf4397375cbe509803/astrobee_api/api/src/main/jav
a/gov/nasa/arc/astrobee/types/Vec3d.java
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee
.types.Quaternion
https://github.com/nasa/astrobee_android/blob/5b07e4d626781
a6f7e0a9cdf4397375cbe509803/astrobee_api/api/src/main/jav
a/gov/nasa/arc/astrobee/types/Quaternion.java
gov.nasa.arc.astrobee
.types.Point
https://github.com/nasa/astrobee_android/blob/5b07e4d626781
a6f7e0a9cdf4397375cbe509803/astrobee_api/api/src/main/jav
a/gov/nasa/arc/astrobee/types/Point.java

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
17
3.2. Building your application
3.2.1. On Ubuntu
To build your application, use the command shown below.
NOTE: DO NOT build your application using Android Studio to change the build task, as
this may cause an error.
$ cd <YOUR_APK_PATH>
$ ANDROID_HOME=$HOME/Android/Sdk ./gradlew assembleDebug
You can find the APK file as “<YOUR_APK_PATH>/app/build/outputs/apk/app-debug.apk”.
3.2.2. On Windows
Please build your application with the following steps.
1) Launch Android Studio.
2) Open <YOUR_APK_PATH>.
3) Click app on the [Project] window.
4) Select [Build] -> [Make Module ‘app’].
If you find errors, please build an APK file on an Ubuntu machine.
You can find the APK file as “<YOUR_APK_PATH>\app\build\outputs\apk\app-debug.apk”.
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
18
3.2.3. Change the application ID (optional)
You can change the application ID (jp.jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc.sampleapk or
jp.jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc.defaultapk by default).
In this step, we change the application ID to “jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc.myteam” and APK name
to “myteam” with the SampleAPK project.
NOTE: This instruction is for the final round. Changing application ID is not necessary
and not recommended in the preliminary round.
NOTE: “jaxa.iss.kibo.rpc” cannot be changed.
1) Launch Android Studio.
2) Open <YOUR_APK_PATH>.
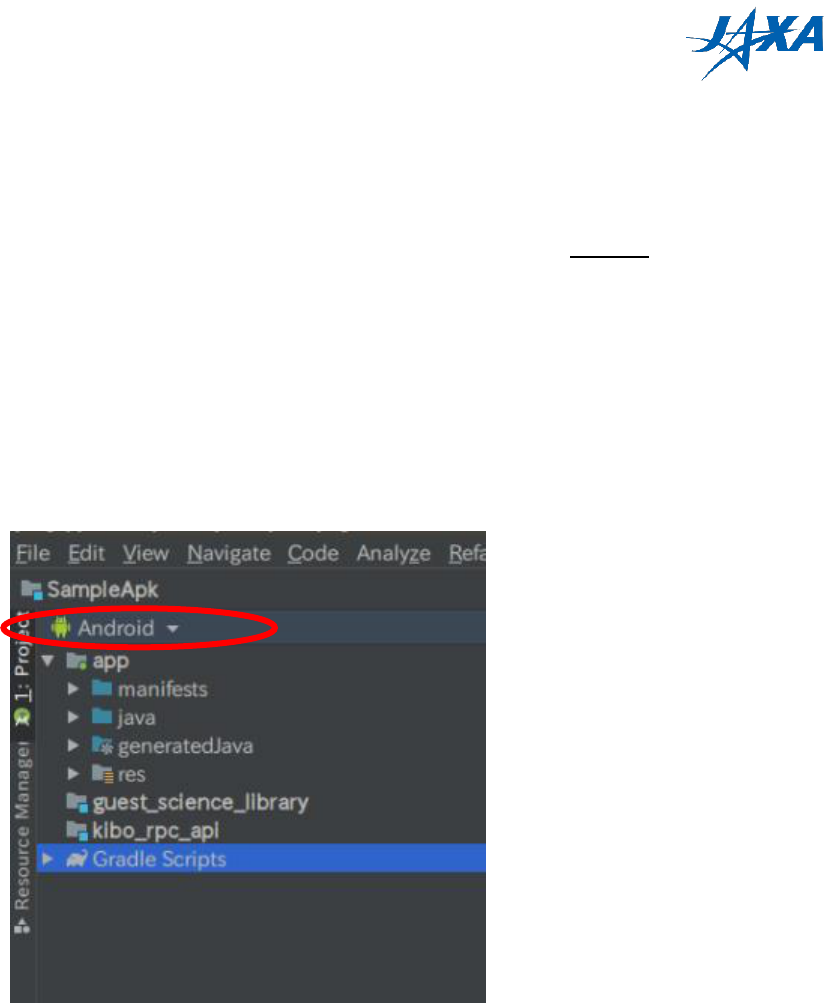
3) Make sure you are viewing the project in Android View.
Figure 3.2-1 Android View
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
19
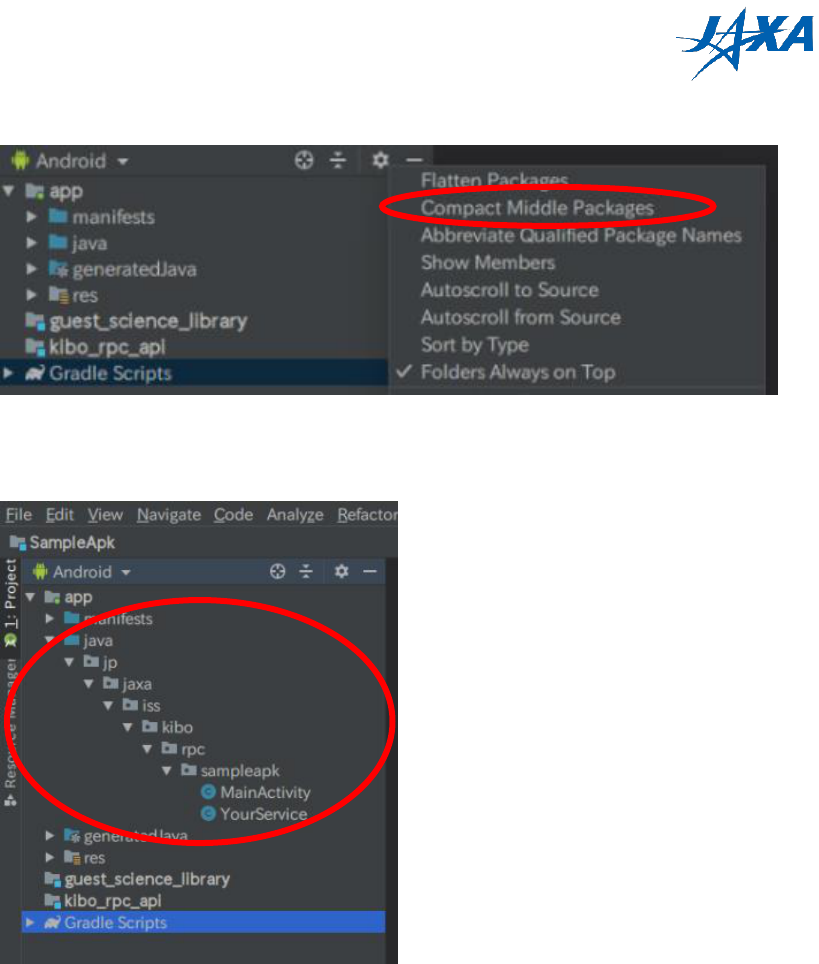
4) Click on the setting gear icon and unselect [Compact Empty Middle Package].
Figure 3.2-2 Unselect [Compact Empty Middle Package]
5) Please expand the “java” folder.
Figure 3.2-3 Expand the “java” folder
6) Right-click the "sampleapk" folder and select [refactor] -> [rename].
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
20
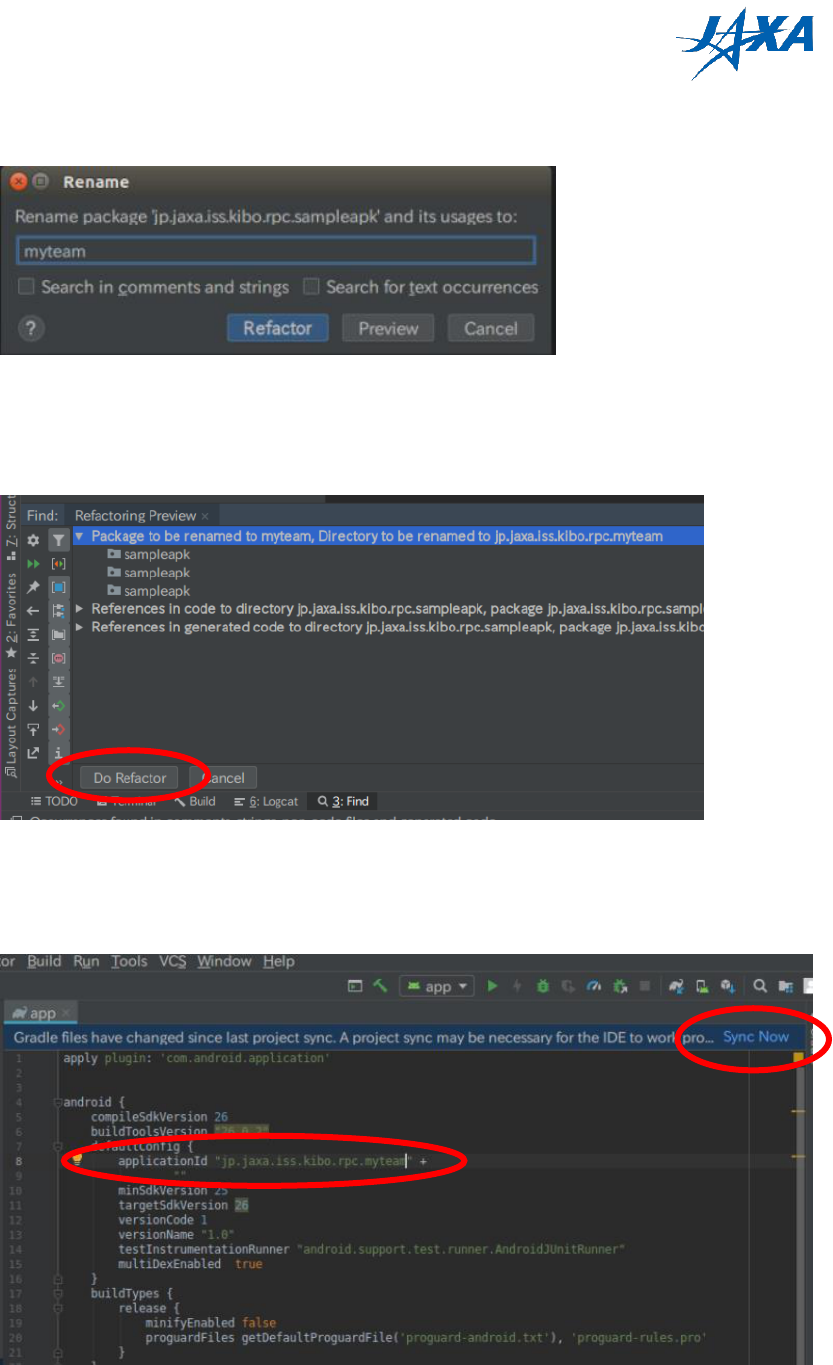
7) A warning will be displayed, but you go ahead and click [Rename Package]. After
that, enter theAPKname that you want. (In the picture, we rename to “myteam”.)
Figure 3.2-4 Rename dialog
8) In the bottom of Android Studio, “Refactoring Preview” will be displayed. Here, click
[Do Refactor].
Figure 3.2-5 Refactoring Preview
9) Open build.gradle (Module: app) in Gradle Scripts on the left-side menu. Please
change the application ID and click [Sync Now].
Figure 3.2-6 build.gradle (Module: app)
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
21
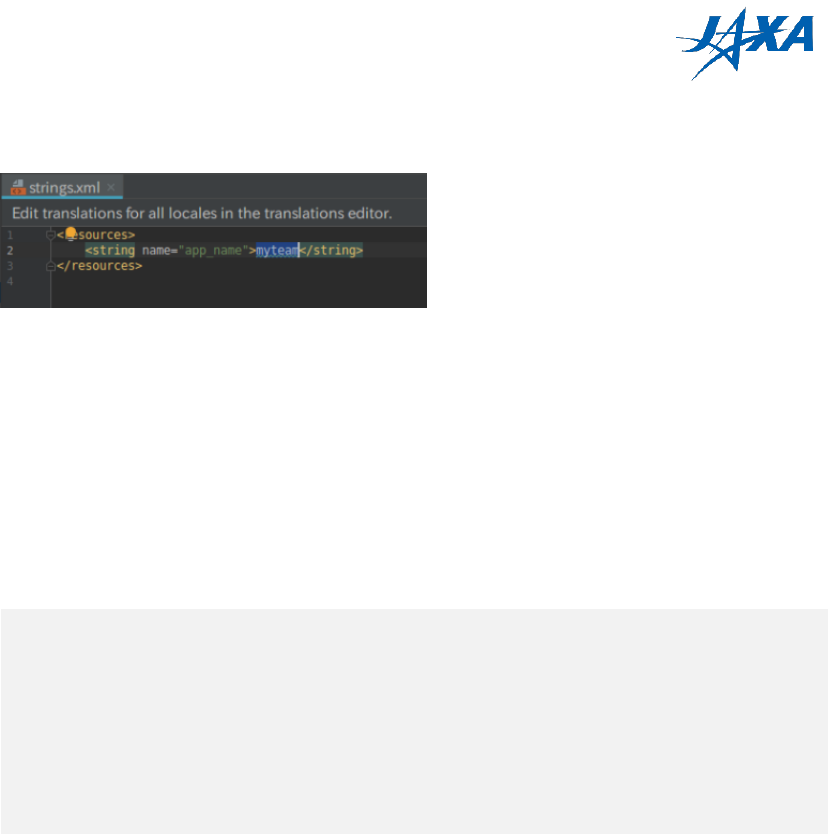
10) Open strings.xml in app -> res -> values on the left-side menu. Please change the
APK name and save.
Figure 3.2-7 strings.xml
You have successfully changed the application ID in Android Studio. And if you want to
change the Android project name and its directory name, follow the next steps.
(1) On Ubuntu
11) Close Android Studio.
12) Please execute the following commands.
cd <YOUR_APK_PATH>
cd ../
mv SampleApk <YOUR_APK_NAME>
cd <YOUR_APK_NAME>
mv SampleApk.iml <YOUR_APK_NAME>.iml
(2) On Windows
10) Close Android Studio.
11) Please rename a SampleApk folder to <YOUR_APK_NAME> with Windows Explorer.
12) Please rename a SampleApk.iml to <YOUR_APK_NAME>.iml in the SampleApk folder
with Windows Explorer.

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
22
4. Running your program on the simulator
4.1. Using the simulator server
Once you have built your application, you can run it with the web simulator provided by
JAXA. To use the simulator, you need a user account issued by the Kibo-RPC secretariat. If
you don’t have one, please read the Kibo-RPC Guidebook to complete your application for
participation in Kibo-RPC first.
4.2. Login
Access the Kibo-RPC web site ( https://jaxa.krpc.jp/ ) and click “LOGIN”.
Figure 4.2-1 LOGIN tab
On the login form, enter the ID and password for your team’s account, and click the
“LOGIN” button. If you have forgotten your ID or password, please contact the Kibo-RPC
secretariat.
Figure 4.2-2 LOGIN button
Now, you can access the web simulator from this page.
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
23
Figure 4.2-3 Web simulator page
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
24
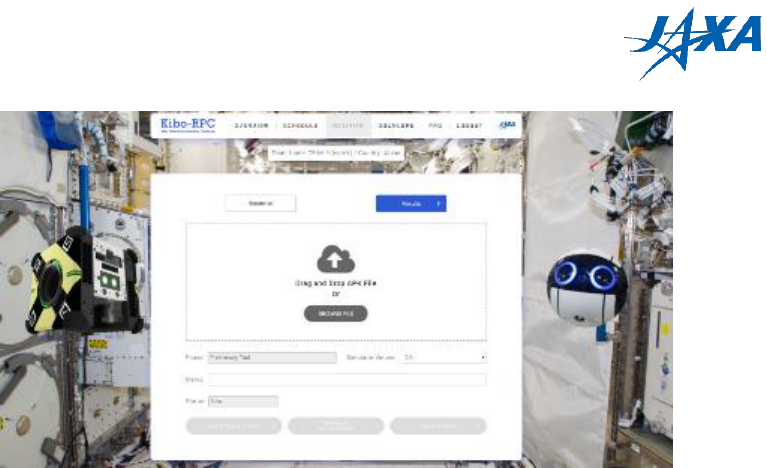
4.3. Uploading the APK and running your program
On the simulation page, select your APK file and the simulator version, enter a memo if
desired, and click the “START SIMULATION” button.
Figure 4.3-1 START SIMULATION button
A simulation may take longer than 20 minutes to run, and it does not need your attention
while it runs. After starting your simulation, for example, you can log out, get a cup of
coffee, then go back to the web site.
When there is a simulation running, the simulation page displays its original information,
so you cannot run another simulation until it finishes.
If you want to stop your simulation, click the “TERMINATE SIMULATION” button. Note
that terminating a simulation loses its game score and output files (such as rosbag and the
Android Emulator’s log).
Figure 4.3-2 TERMINATE SIMULATION button
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
25
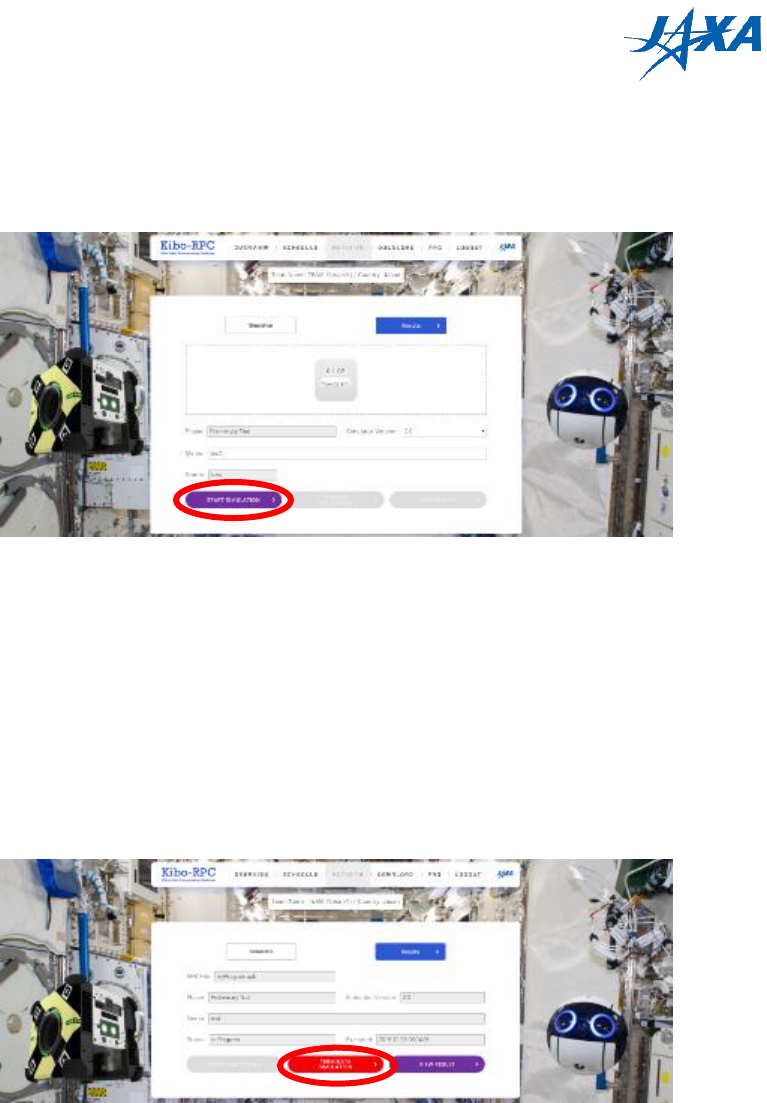
4.4. Checking simulation while running
When your simulation is running, you can log in to the simulator server (viewer) via your
browser. Click the “SIMULATIOR VIEWER” button to show the information for a remote
connection, and open the viewer in another tab by clicking the “VIEW” button.
Figure 4.4-1 VIEW button
Enter the password for your remote connection to log in. Now you can use rviz to see
how Astrobee moves in your simulation. This viewer is available until the simulation is
finished.
The viewer displays a real-time simulation in the view-only mode for the simulation
stability. You cannot operate the viewer..
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
26
4.5. Checking the result
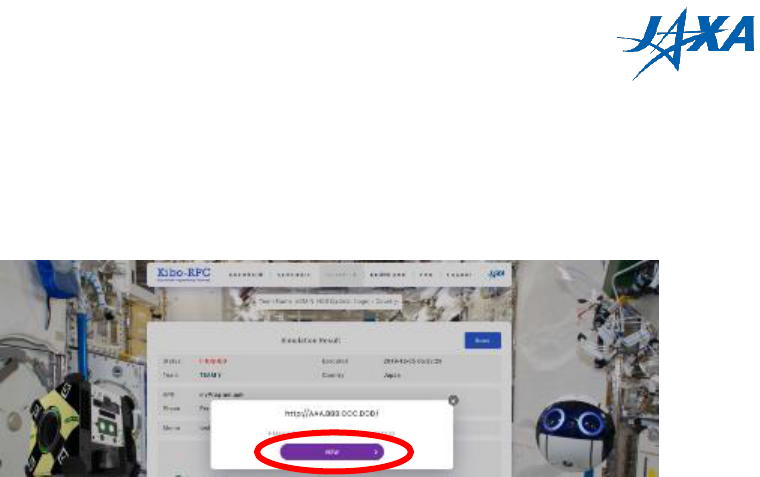
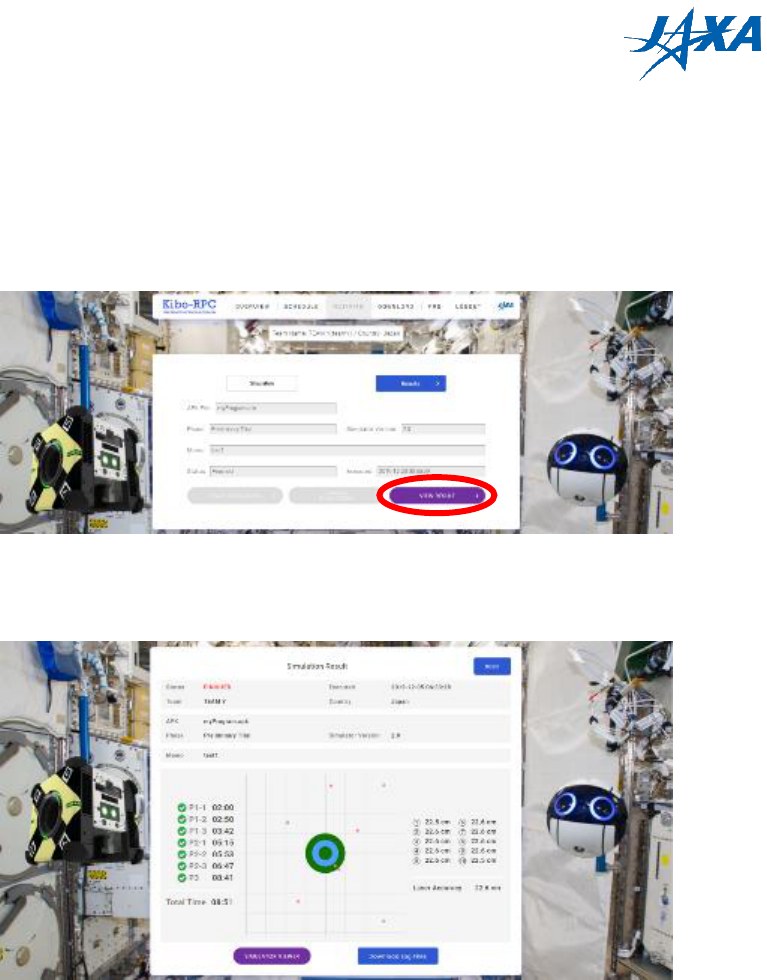
4.5.1. Result summary
Once your simulation has started, you can check the results by clicking the “VIEW
RESULT” button on the simulation page.
Figure 4.5-1 VIEW RESULT button
On the result page, you can see the details of your simulation, such as the game time,
laser accuracy, and so on.
Figure 4.5-2 RESULT page

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
27
4.5.2. Download ZIP file
You can get a ZIP file by clicking the “DOWNLOAD LOG FILES” button. This ZIP file
contains a game score, rosbag and the Android Emulator’s log. Note that some or all of
these files will not be available unless your simulation finishes properly. Besides the result
page, the game score also appears in a JSON file, which can be read using a text editor.
{
"QR": {
"0": {
"result": true,
"timestamp": "19700101 000423792",
:
},
:
},
"AR": {
"result": true,
"timestamp": "19700101 000552624",
:
},
"Approach": {
"0": {
"direction": true,
"x": 1.22,
"y": -3.44,
"r": 4.12,
"timestamp": "19700101 000646960",
:
},
:
},
"Mission Time": {
"start": "19700101 000021632",
"finish": "19700101 000822824"
}
}
“result” is true if the value of the QR
code is correct.
“0”, “1”, … and ”5” correspond to P1-
1, P1-2, … and P2-3.
“result” is true if the marker ID of the
AR tag near Target is correct.
“direction” is true if the laser shot is
on the Target plane.
“r” is the distance between the center
of Target and the laser shot.
“0”, “1”, … and “9” correspond to the
1
st
, 2
nd
, … and 10
th
snapshot.
The average distance is referred to
as “Laser Accuracy”.
“Game Time” is the difference
between the “start” time and the
“finish” time.
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
28
4.5.3. Check simulation after running
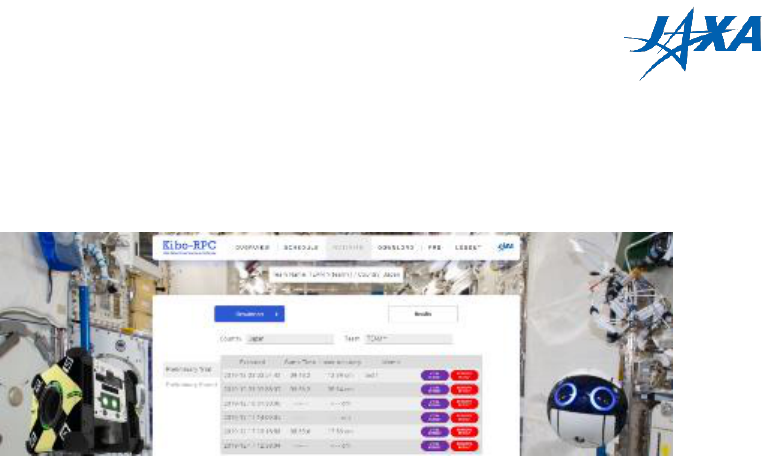
To check previous simulations, click the “Results” button on the simulation page. The
results page lists your past simulations. This list can hold up to 20 simulations.
Figure 4.5-3 Results list page
The “VIEW RESULT” button is the same as the one on the simulation page. Please be
careful when you click the “REMOVE RESULT” button; it removes the output files of the
selected simulation and the removed result will be lost.
You can play the rosbag (simulation result) at 0.5x – 3x speed with the viewer. You can
change rosbag replay settings and rviz settings. In detail, it is described below sections.
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
29
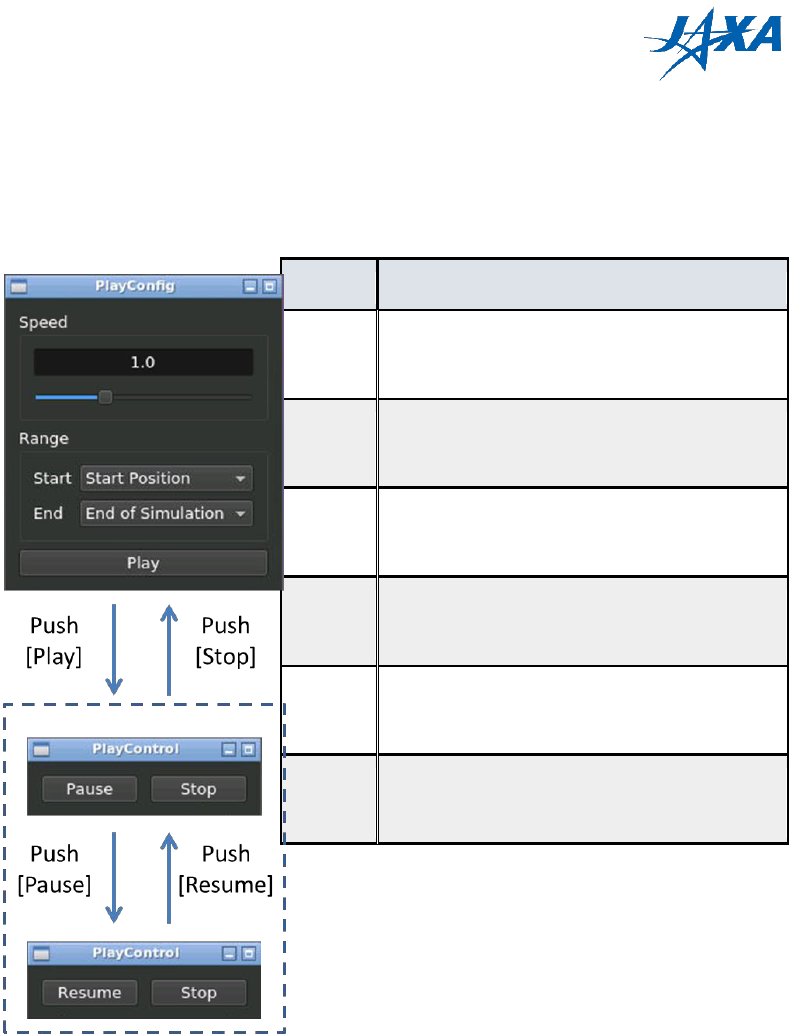
4.5.4. rosbag replay settings
You can change rosbag replay settings using Rosbag Player.
Figure 4.5-4 Rosbag Player
Type
Description
Speed
Slider
Select replay speed.
Range
Selector
Select replay range.
Play
Button
Start replay and open rviz window.
If rviz already has opened, it will restart.
Pause
Button
Pause replay.
Resume
Button
Resume replay.
Stop
Button
Stop replay and back to PlayConfig
window.
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
30
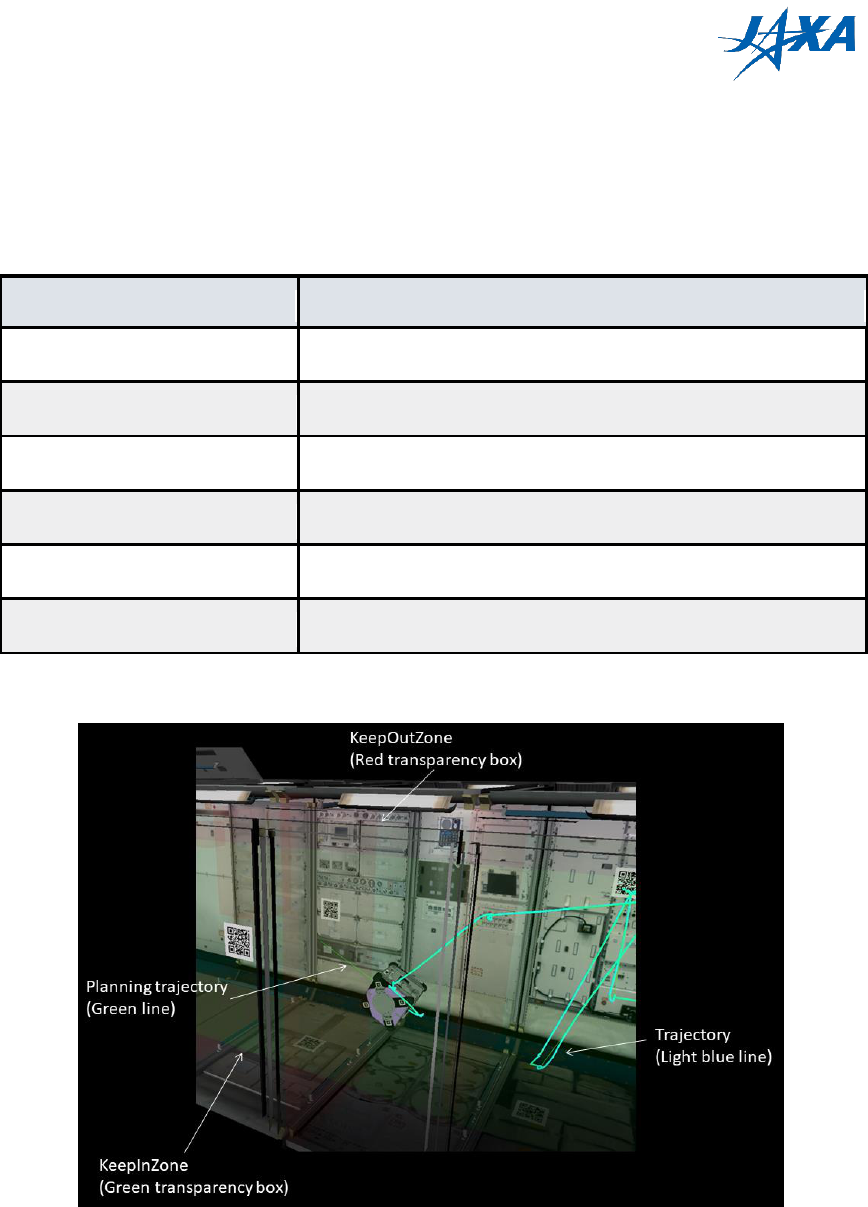
4.5.5. rviz settings
You can change display settings on rviz window.
Table 4-1 rviz configuration
Item
Check box in the “Displays” tab
Planning trajectory
[Visualize]->[PlanningTrajectory]
Trajectory
[Visualize]->[Trajectory]
KeepInZone/KeepOutZone
[Visualize]->[Zones]
NavCam
[Sensors]->[NavCam]
DockCam
[Sensors]->[DockCam]
HazCam
[Sensors]->[HazCam]
Figure 4.5-5 rviz configuration description

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
31
4.6. Running on your own machine (optional)
You can also run the program on your own machine. This chapter provides a procedure
to set up the Astrobee simulator. You get a simple simulation environment without
randomness modules (Air flow simulator and Objects randomness generator) or judge
module.
4.6.1. Differences between web simulator and local
simulator
External Modules for Local Simulation Environment does not include random factor
modules (Object position, airflow and navigation error).
You can test and debug your program using local simulator, but need to evaluate it on
web simulator server in order to obtain a high score in the preliminary round.
4.6.2. Requirements
The following requirements are needed to set up a simulation environment on your
machine.
64-bit processor
8 GB RAM (16 GB RAM recommended)
Ubuntu 16.04 (64-bit version) ( http://releases.ubuntu.com/16.04/ )
4.6.3. Setting up the Astrobee Robot Software
Clone code from GitHub ( https://github.com/nasa/astrobee ) and install Astrobee Robot
Software according to the installation manual.
( https://github.com/nasa/astrobee/blob/70e3df03ff3f880d302812111d0107f3c14dccc0/INS
TALL.md )
NOTE: Since the web simulator is running Astrobee Robot Software v0.10.2 and
Android submodule v0.8.0, so please execute the following command after clone the
android software repository.
pushd $SOURCE_PATH
git checkout 70e3df03ff3f880d302812111d0107f3c14dccc0
popd
pushd $ANDROID_PATH
git checkout 5b07e4d626781a6f7e0a9cdf4397375cbe509803
popd
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
32
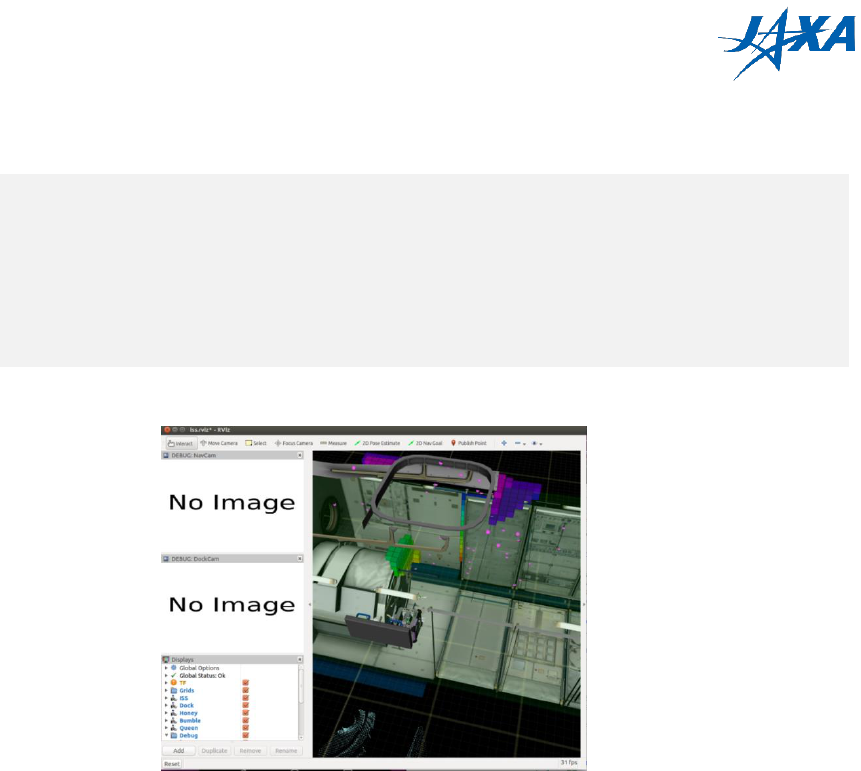
After building the source code, execute the following commands in order.
pushd $BUILD_PATH
source devel/setup.bash
popd
roslaunch astrobee sim.launch dds:=false robot:=sim_pub rviz:=true
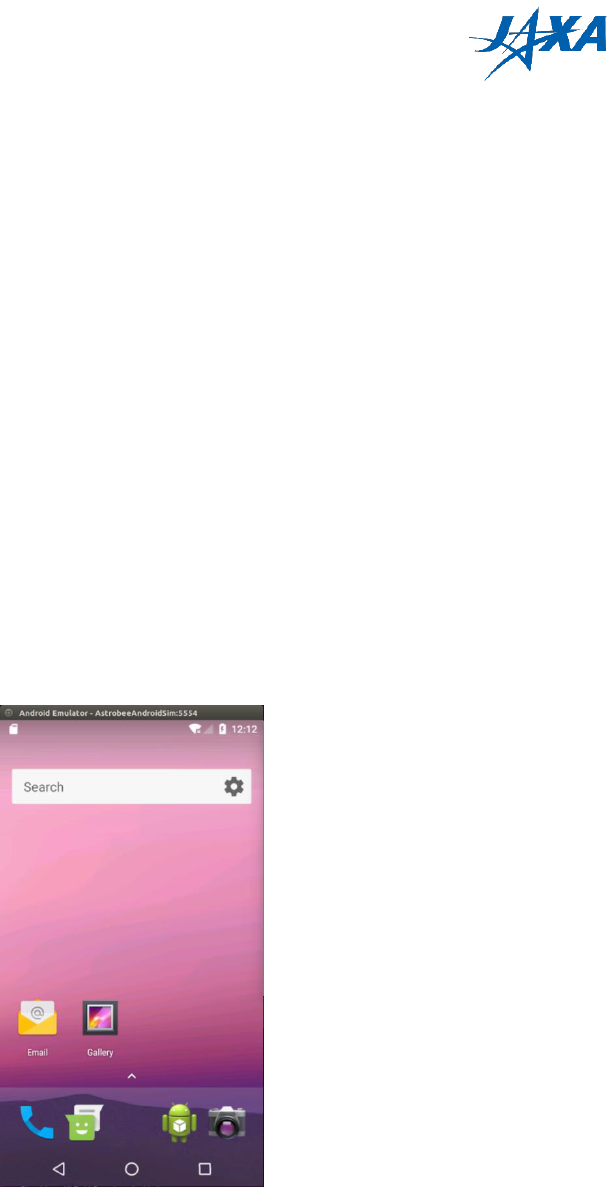
Is the image below displayed on your screen? If so, installation is complete!
Figure 4.6-1 Setup result
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
33
4.6.4. Creating the AVD ( Android Virtual Device )
Create an AVD ( Android Virtual Device ) as follows.
1) Launch Android Studio.
2) Select [Tools] -> [AVDManager].
3) In the Android Virtual Device Manager Window, click [+ Create Virtual Device …].
4) Select device Nexus 5 ( Resolution 1080x1920 ) and click [Next].
5) Select the [x86 Images] tab, choose Nougat/API Level 25/ABI x86_64/Android
7.1.1(NO Google APIs), then click [Next].
NOTE: Download the system image if you need it.
6) Set the AVD name to “AstrobeeAndroidSim”.
7) Click [Finish].
In the Android Virtual Device Manager window, you will see “AstrobeeAndroidSim” in the
list.
Click the Play button in the Action column. If the AVD launches successfully, the
following image is displayed.
Figure 4.6-2 Android emulator screen
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
34
4.6.5. Building the Guest Science Manager APK
To run your program, you must install the Guest Science Manager APK. (Details at
https://github.com/nasa/astrobee_android/blob/5b07e4d626781a6f7e0a9cdf4397375cbe50
9803/guest_science_readme.md )
Execute the following commands in order to build the Guest Science Manager APK.
cd $ANDROID_PATH/core_apks/guest_science_manager
$ ANDROID_HOME=$HOME/Android/Sdk ./gradlew assembleDebug
4.6.6. Setting up the network
Setup the network between the Astrobee Simulator and the Android Emulator.
(1) Setting the HOST network
Execute the following commands to open the host file.
sudo nano /etc/hosts
Add 3 lines bellow to the host file and save.
10.42.0.36 hlp
10.42.0.35 mlp
10.42.0.34 llp
(2) Setting the environment variables
Execute the following commands to set the environment variables.
export ANDROID_PATH="${SOURCE_PATH}_android"
export EMULATOR=$HOME/Android/Sdk/tools/emulator
export AVD=" AstrobeeAndroidSim”
Note that you need to execute the above commands whenever you open a terminal. If
you write thees commands in your .bashrc file, you don’t have to execute them.

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
35
(3) Setting up the Android network and starting the Android
Emulator
Execute the following commands to set up the Android network and launch the Android
Emulator.
cd $ANDROID_PATH/scripts
./launch_emulator.sh -n
4.6.7. Installing APKs
If the Android Emulator is not running, execute the following commands to start it.
cd $ANDROID_PATH/scripts
./launch_emulator.sh -n
In another terminal, execute the following commands to install the Guest Science
Manger APK and your GS APK.
cd $ANDROID_PATH/core_apks/guest_science_manager
adb install -g -r activity/build/outputs/apk/activity-debug.apk
cd <YOUR_APK_PATH>
adb install -g -r app/build/outputs/apk/app-debug.apk
4.6.8. Setting QR codes, an AR tag, and the target
Set QR codes, an AR tag and the target in the Astrobee Simulator in the following steps.
1) Download Kibo-RPC_SimExtMod.zip from the Download page on the Web site.
2) Extract the zip file to directory you want.
3) Execute the following commands.
cd <SETUP MODULE DIR>
chmod +x setup.sh
./setup.sh
Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
36
4.6.9. Running your program
It's time to run your program!
(1) Launching the Android Emulator
Execute the following commands to launch the Android Emulator.
cd $ANDROID_PATH/scripts
./launch_emulator.sh -n
(2) Starting the Astrobee Simulator
Before starting the Astrobee Simulator, execute the following commands to set the ROS
Environment Variables on the other terminal.
export ROS_IP=$(getent hosts llp | awk '{ print $1 }')
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://${ROS_IP}:11311
Execute the following command to start the Astrobee Simulator.
roslaunch astrobee sim.launch dds:=false robot:=sim_pub rviz:=true

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
37
(3) Running the Guest Science Manager APK and GS APK
Execute the following commands to set the ROS Environment Variables on the other
terminal again.
export ROS_IP=$(getent hosts llp | awk '{ print $1 }')
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://${ROS_IP}:11311
Execute the following commands to start the Guest Science Manager APK and to
launch the GDS simulator.
$ANDROID_PATH/scripts/gs_manager.sh start
cd $SOURCE_PATH/tools/gds_helper/src
python gds_simulator.py
Operate the GDS simulator to run your GS APK.
1) Press any key to grab control
2) Select your GS APK.
3) Type b and press Enter to start the GS APK.
4) Type d and press Enter to send a custom guest science command.
Then Astrobee starts to locate the leak!

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
38
5. Programming tips
5.1. Do NOT write infinite loops
You must not write any infinite loops in your code because no one can stop Astrobee
while the loop is executing.
You should use finite loops with a defined counter value as shown below.
// NG
while(!result.hasSucceeded()){
// do something
}
// OK
final int LOOP_MAX = 5;
int loopCounter = 0;
while(!result.hasSucceeded() && loopCounter < LOOP_MAX){
// do something
++loopCounter;
}

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
39
5.2. Dealing with randomness
You must consider the randomness of the environment.
When you want to move robot below…
// move to point 1
api.moveTo(point1, quaternion1, true);
// move to point 2
api.moveTo(point2, quaternion2, true);
// move to point 3
api.moveTo(point3, quaternion3, true);
If there is no randomness in the environment, this code works well.
However, Astrobee may be faced with errors such as tolerance violations and your
code will not work.
So, you have to provide the redundant code as we see below.
Remember, Do NOT allow any infinite loops in your code!
Result result;
final int LOOP_MAX = 5;
// move to point 1(first try)
result = api.moveTo(point1, quaternion1, true);
// check result and loop while moveTo api is not succeeded.
// Do NOT write infinite loop.
int loopCounter = 0;
while(!result.hasSucceeded() && loopCounter < LOOP_MAX){
// retry
result = api.moveTo(point1, quaternion1, true);
++loopCounter;
}
// move to point 2
//…

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
40
5.3. Camera parameters
If you would like to use camera parameters, you can use the ones given below.
camera_matrix:
rows: 3
cols: 3
data: [344.173397, 0.000000, 630.793795, 0.000000, 344.277922, 487.033834, 0.000000,
0.000000, 1.000000]
distortion_model: plumb_bob
distortion_coefficients:
rows: 1
cols: 5
data: [-0.152963, 0.017530, -0.001107, -0.000210, 0.000000]
5.4. About navigation error
The real world always has uncertainties.Navigation error is one of them and Kibo-RPC
simulator server simulates it.
However, modeling and simulating navigation error completely are complicated and the
calculation load becomes higher,therefore random error following gaussian distribution is
used generally.
Kibo-RPC simulator also implements gaussian distribution and the parameters are as
follows;
Regarding position;
x: mean = 0 m and 3sigma = 0.1 m
y: mean = 0 m and 3sigma = 0.1 m
z: mean = 0 m and 3sigma = 0.1 m
Regarding orientation;
x: mean = 0 degree and 3sigma = 3 degree
y: mean = 0 degree and 3sigma = 3 degree
z: mean = 0 degree and 3sigma = 3 degree
You have to consider that self-position and self-orientation obtained from API
(getTrustedRobotKinematics and getTrustedRobotKinematics) includes these error.

Version 2.3.3
Released Date: August 21
st
, 2020
41
6. Simulator change log
Ver.1.0
Initial Release
Ver.2.0
Add airflow module as a disturbance element.
Add Keep In Zone and Keep Out Zone.
Add simulation playback function.
Visualize of planned path and actual path.
Ver.2.1
Add navigation error as a random factor.
* The version which will be used in preliminary round is the latest version.